EPITHALON
Epithalon has been shown to influence cellular longevity, circadian biology, and oxidative balance. Unlike direct hormones, Epithalon regulates the underlying processes tied to the body's aging and repair.
EPITHALON OVERVIEW
Category: Synthetic Tetrapeptide, Geroprotector, Pineal Peptide
How It Works: stimulates the natural production of telomerase. Which helps maintain and repair telomeres.
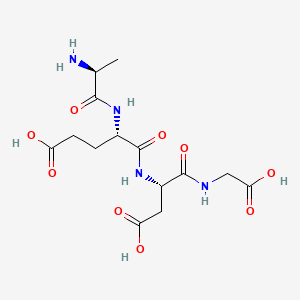
Chemical Structure: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly
Alternative Names: Epitalone, Epitalon, The Anti-Aging Peptide
CAS Number: 307297-39-8
WHAT IS EPITHALON
Epithalon is a short, synthetically produced tetrapeptide originally synthesized based on the naturally occurring polypeptide extracted from the pineal glands of cattle, Epithalamin. The primary hypothesis finds that Epithalon serves a regulatory role in the pineal gland's endocrine and aging systems. Originally developed by a Russian gerontologist, Vladimir Khavinson, Epithalon has been studied for its ability to regulate aging, improve circadian rhythms, and activate telomerase, a key enzyme tied to DNA protection and cellular longevity.
WHAT DOES EPITHALON DO?
Epithalon exerts its effects by influencing cellular longevity, circadian biology, and oxidative balance. Unlike hormones that act directly, Epitalon regulates underlying processes tied to aging and repair.
Epithalon is viewed by researchers as a core component in the endocrine theory of aging. Its observed effects stem from its modular action on key biological processes:
-
Telomerase Activation: The central mechanism is the induction of telomerase enzyme activity. Telomerase is responsible for lengthening telomeres (the protective caps on chromosomes). Telomere shortening is a recognized hallmark of cellular aging and senescence. By promoting telomerase activity, Epithalon is theorized to extend the proliferative capacity and lifespan of somatic cells.
-
Pineal Gland Function: It acts on the pineal gland to restore or normalize the gland's function, particularly its production of the hormone melatonin. This correction helps normalize the circadian rhythm.
-
Gene Expression and Homeostasis: Research suggests Epithalon influences the expression of certain genes related to cell proliferation, apoptosis (programmed cell death), and the immune system, helping to restore cellular and systemic homeostasis.
-
Antioxidant Effects: It exhibits properties as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, protecting against cellular damage caused by oxidative stress.
BENEFITS/ CLINICAL TRIALS
Epithalon has been subjected to decades of research, primarily out of Russia. The scope has focused on its geroprotective and endocrine-normalizing properties.
Key Benefits:
- Increase in cellular lifespan:
- The potential benefits of Epithalon in preventing cellular degradation, thanks to its ability to lengthen telomeres, are very notable. As age increases, the pineal glands' function diminishes, leading to a disruption in sleep patterns, hormonal balances, and decreased melatonin production. By lengthening telomeres, Epithalon has been shown to regenerate the pineal gland and, as a byproduct, normalise circadian rhythms and improve overall sleep quality, improving cognitive function, mood stability, and overall wellbeing.
- Lifespan Modulation:
- Multiple studies have demonstrated an increase in average lifespan and maximum lifespan compared to the control tests.
- Immune System Modulation:
- Another significant benefit is its ability to modulate the immune system. Aging often leads to immunosenescence, characterized by a decline in immune function and an increased susceptibility to infections and diseases. By boosting the activity of immune cells, Epithalon enhances the body's ability to fight off pathogens and reduce the risk of autoimmune disorders.
- Pathology and Oncology:
- Research has suggested that it has the potential to inhibit the development of certain spontaneous and induced tumors, as well as other age-related pathologies.
While human trials have been conducted on small cohorts, results are primarily focused on biomarkers and quality of life rather than definitive lifespan extension:
-
Human studies have reported that Epithalon treatment improved parameters like T-cell function (an aging immune marker) and normalized melatonin production in elderly patients.
-
Long-term monitoring of patients receiving Epithalon for age-related pathology suggests positive modulation of several markers associated with biological age. However, these are often limited in scope and methodology compared to Western Phase 3 trials.
SIDE EFFECTS
Epithalon is widely regarded in the research community as having a very low acute toxicity profile.
-
Toxicity: Acute and long-term toxicity tests in animal models have historically shown no detrimental systemic side effects.
-
CNS/Systemic Effects:
-
Mild, transient headache or dizziness, particularly upon initial administration.
-
Temporary feeling of increased energy or alertness (due to pineal modulation).
-
-
Local Reactions:
-
Injection Site Reactions such as transient pain, redness, or swelling.
-
-
Mental/Psychological: No reports of mood alteration, dependency, or withdrawal symptoms have been substantiated in the reviewed literature.
IS EPITHALON SAFE?
Epithalon is not approved by the FDA or any major global regulatory authority for therapeutic use.
Despite the promising toxicity data from preclinical and non-Western clinical research, large-scale, independent human clinical trials are necessary to fully assess its long-term safety, particularly concerning the cumulative effects of telomerase activation and cell proliferation over decades. It remains an experimental geroprotective agent.
While Epitalon is widely regarded as safe and well-tolerated, it's important to understand potential side effects and precautions before beginning use.
DOSAGE
The typical protocol involves 1 to 3 mg per day for 10 to 20 consecutive days, followed by a break. Some anti-aging practitioners recommend repeating this cycle biannually. Alternatively, a maintenance dose of 1 mg per day taken intermittently throughout the year has also been suggested in longevity communities.
It is typically taken subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
RECONSTITUTION
Epithalon is supplied as a lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder and requires reconstitution with sterile water.
-
Reconstitution Fluid: Use sterile or bacteriostatic water.
-
Standard Dilution: For a 10 mg, adding 1 mL of BAC water results in a highly concentrated stock solution of 10 mg/mL (10,000 mcg/mL).
-
Mixing Technique: Inject the BAC Water slowly down the side of the vial. DO NOT SHAKE vigorously. Gently swirl or roll the vial between your hands for several minutes until the powder is completely dissolved and the solution is clear.
-
Post-Reconstitution Storage: Once reconstituted, the solution must be stored in the refrigerator 2C to 8C or 36°F to 46°F and is typically stable for 14 to 28 days.
WHERE TO BUY EPITHALON
Researchers should always vet their sources to ensure that a few key factors are present in their test subjects. With the rise in peptide popularity in recent years, many companies have created peptides that undergo little to no testing, quality standards, or regulations. As it is not regulated by the FDA, researchers must do their due diligence and look closely at the company's practices and standards.
When selecting a supplier for Epithalon, focus on transparency and quality assurance, not customer testimonials:
- Quality Documentation: A reputable supplier must provide:
- Certificate of Analysis (COA): This document must be recent (corresponding to the batch/lot number purchased) and demonstrate a minimum purity of >95% via High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) testing.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS) Data: The COA must include mass spectrometry (MS) confirmation to verify the compound’s exact molecular weight, confirming its chemical identity.
- Contaminant Testing: Look for reports on heavy metals, microbial load, and solvent residues (e.g., residual trifluoroacetic acid, or TFA). The presence of these contaminants can severely compromise research and introduce unknown toxicity.
- Vendor Verification and Transparency
-
Specialization: Prioritize vendors who specialize in the manufacturing and distribution of peptides for academic and biotechnology research, rather than general supplement vendors.
-
Manufacturing Origin: Inquire about the source of the raw materials and the manufacturing protocols. Ideal suppliers adhere to strict quality control processes.
-
Handling & Storage: The supplier must provide clear documentation on the proper storage and handling procedures for the peptide to maintain its stability and integrity.
-
Conclusion on Procurement: Given the high risk of contamination, mislabeling, and legal ambiguity. The use of Epithalon outside of this defined research context poses unacceptable, unquantified risks to human health.
REFERENCES
-
Hoang, Tuan, et al. “Experiments on Synchronous Nonlinear Features for 2-Class NIRS-Based Motor Imagery Problem.” University of Canberra Research Portal, Springer, 1 Jan. 1970, researchprofiles.canberra.edu.au/en/publications/experiments-on-synchronous-nonlinear-features-for-2-class-nirs-ba
-
by, Written. “Unlocking the Secrets of Epitalon: The Anti-Aging Peptide Revolutioniz.” Swolverine, swolverine.com/blogs/blog/unlocking-the-secrets-of-epitalon-the-anti-aging-peptide-revolutionizing-longevity. Accessed 12 Nov. 2025.
-
“Epitalon.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Epitalon. Accessed 12 Nov. 2025.
-
Anti-Aging Therapeutics. "The role of the pineal peptide Epithalon in the control of telomere length and aging."
-
International Journal of Molecular Sciences. "Tetrapeptide $\text{Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly}$ (Epithalon) restores the telomerase activity in human cells."
-
Biogerontology. "Peptide regulation of functional activity of the pineal gland in aging."
-
Neuro Endocrinol Lett. "The effect of the peptide Epithalon on biomarkers of aging in elderly subjects."
-
Journal of Experimental and Clinical Medicine. "Peptide-based drugs regulating the aging process."
The PrepTide: Disclaimer

