MOTS-C
MOTS-c is a peptide that regulates gene expression related to metabolic homeostasis and cellular stress. By stimulating glucose uptake, MOTS-c helps cells utilize glucose for energy, thus supporting metabolic health and function.

MOTS-C OVERVIEW
Category: Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide, Metabolic Regulator, Exercise Mimetic
How It Works: MOTS-c is a peptide that regulates gene expression related to metabolic homeostasis and cellular stress. By stimulating glucose uptake, MOTS-c helps cells utilize glucose for energy, thus supporting metabolic health and function.
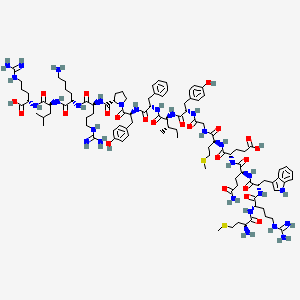
Chemical Structure: Met-Arg-Trp-Gln-Glu-Met-Gly-Tyr-Ile-Phe-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Lys-Leu-Arg(16 AAs)
Alternative Names: Mitochondrial ORF
CAS Number: Not Applicable
WHAT IS MOTS-C
MOTS-c is a small 16-amino acid peptide with a singular distinction: it is one of a handful of known Mitochondrial-Derived Peptides (MDPs).
-
Genetic Code: Unlike most peptides, which are coded by the nuclear genome, MOTS-c is encoded by a short open reading frame (sORF) within the mitochondrial genome (mtDNA), specifically the 12S rRNA region.
-
Cellular Function: The mitochondria are the “power generators” in cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use (ATP). MOTS-c plays a role in this energy regulation, often acting as a signaling molecule between the mitochondria and the rest of the cell.
WHAT DOES MOTS-C DO?
MOTS-c acts as a metabolic coordinator, linking mitochondrial health to nuclear gene expression, a critical communication system that often fails during aging and metabolic disease. Mitochondrial-derived peptides like MOTS-c have a role in maintaining mitochondrial function and protecting cells under different stresses.
Dual Mechanism and Key Benefits
-
AMPK Activation (Metabolic Switch): MOTS-c is a potent activator of AMPK (AMP-Activated Protein Kinase), the cell's master energy sensor. Activation of AMPK drives fatty acid oxidation and stimulates glucose uptake into skeletal muscle cells, mimicking the beneficial effects of exercise and the diabetes drug Metformin.
-
Insulin Sensitization: Its primary metabolic benefit is increasing skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity and promoting GLUT4 translocation, which drives glucose clearance from the blood.
-
Mitochondrial-Nuclear Communication: Under conditions of metabolic stress or exercise, MOTS-c translocates to the nucleus, where it regulates the expression of nuclear genes associated with stress adaptation and homeostasis.
-
Physical Performance and Muscle Preservation: Exercise causes MOTS-c levels to go up in humans. Studies in mice have shown that MOTS-c treatment improves physical performance in mice of all ages and regulates skeletal muscle metabolism and gene expression. Furthermore, MOTS-c has been shown to reduce signaling from Myostatin (a negative regulator of muscle growth) and inhibit pathways that cause muscle wasting (sarcopenia).
BENEFITS/ CLINICAL TRIALS
MOTS-c is a highly active research peptide with implications across numerous age-related conditions. With its combined effects on cellular metabolism, stress response, and longevity, MOTS-c has many of the same therapeutic uses as growth hormone secretagogues (for EXAMPLE: CJC-1295, ipamorelin, and tesamorelin).
Most of the clinical research has been conducted in rodent models, but the biological similarities between rodents and humans present a promising picture of how MOTS-c might impart systemic health benefits.
Key Benefits Observed in Research Models
Improved Metabolic Function and Reduced Body Fat
-
Metabolic Switch: Recall that MOTS-c activates a pathway called AMPK that stimulates glucose uptake. This mechanism allows cells to use glucose more efficiently, and the body can more effectively modulate insulin action.
-
Insulin Action: Conclusions from a 2015 paper noted that MOTS-c has "physiological similarities to the first-line diabetes drug Metformin" with regard to managing glucose utilization, metabolism, and body weight.
-
Obesity Prevention: In a group of mice fed a high-fat diet, MOTS-c appeared to prevent obesity onset. Other studies corroborated these results, finding that higher plasma MOTS-c levels are negatively correlated with obesity.
-
Fat and Liver Health: MOTS-c prevents diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance, reduces hepatic fat accumulation, and shows potential for treating MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease).
Improved Physical Performance and Endurance
-
Exercise Mimicry: Recall that endogenous MOTS-c can be activated by exercise. Exogenous MOTS-c has been shown to have the same performance-enhancing effect. In one study, MOTS-c significantly enhanced physical performance and running time (approximately 12 percent to 15 percent increase) in mice of all ages, suggesting it can confer exercise benefits without physical activity.
-
Human Correlation: Findings from a 2023 human study found that a higher serum MOTS-c concentration correlated with "greater muscle mass, force, and power generated during jumping" in healthy subjects.
Anti-Inflammation and Bone Health
-
Reduced Inflammation: A 2024 study on mice demonstrated antiallodynic effects, meaning the treatment alleviated pain caused by stimuli that wouldn’t normally induce pain. It significantly ameliorated inflammatory factors and responses, leading researchers to conclude that MOTS-c "may serve as a promising therapeutic target for inflammatory pain."
-
Bone Growth: MOTS-c promotes osteoblast proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization. Osteoblasts form new bones and heal existing ones, suggesting MOTS-c’s action is beneficial for anyone at high risk of developing osteoporosis, such as postmenopausal women.
Longevity and Quality of Life
-
Aging and Lifespan: Treatment initiated in late life in mice improved overall physical capacity and showed a trend toward increasing both median and maximum lifespan.
-
Quality of Life: By attenuating factors associated with advanced age metabolic dysfunction, increased body fat, decreased physical capacity, increased inflammation, and reduced bone density, MOTS-c supports a more robust and enjoyable aging experience.
Clinical Trial Findings
-
Formal Clinical Trials: MOTS-c is currently restricted to preclinical and early Phase 1 research. Analogs of MOTS-c are being developed by pharmaceutical companies for obesity and fatty liver disease, confirming significant translational interest.
-
Human Data: Endogenous plasma levels of MOTS-c are observed to increase following human exercise, linking it directly to exercise biology. Levels also typically decline with age, consistent with the hypothesis that replenishment may support metabolic health.
SIDE EFFECTS
MOTS-c is generally well-tolerated in controlled animal research, often showing no effect on metabolically healthy subjects. Side effects are typically mild and transient.
Common and Transient Side Effects
Preliminary reports suggest mild and transient side effects, many of which are general symptoms associated with injectable peptides:
-
Local Reactions: Injection site irritation, including redness, slight swelling, or discomfort.
-
Neurological: Headache or dizziness.
-
Gastrointestinal: Mild nausea or stomach discomfort.
-
General Systemic: Fatigue.
Less Common and Unknown Risks
Some effects have been reported in unregulated online use, suggesting caution:
-
Other General Symptoms: Insomnia, fever, or increased heart rate/palpitations have been reported.
-
Unknown Risks: Given its influence on fundamental metabolic processes (AMPK) and mTOR regulation, the long-term safety of chronic, supraphysiological MOTS-c administration is unknown and requires caution.
IS MOTS-C SAFE?
MOTS-c is an unapproved research peptide without FDA certification. Its safety profile is currently incomplete, as human trials and controlled use cases are lacking.
Tolerability and Preliminary Safety Data
-
Short-Term Tolerability: Scientific opinion seems to lean toward "safe" rather than "unsafe" based on initial, limited data. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on CB4211, which is an analog (synthetic version) of MOTS-c, found the compound to be "safe and well tolerated" under a single and multiple ascending dose protocol in adult humans. Theoretically, MOTS-c should pose a similar set of risks.
Critical Health Risks
-
Cancer Risk (CRITICAL WARNING): The most alarming risk is its cancer risk. While some research suggests MOTS-c may be useful as a cancer therapy, other studies contradict this, claiming it can lead to the development of prostate and breast cancer. Clinical researchers warn that people with an active cancer diagnosis should avoid MOTS-c unless otherwise recommended by their doctor.
-
WADA Prohibition: MOTS-c is currently prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) under the category of AMPK Activators and metabolic modulators.
Safety Takeaway
Due to incomplete safety data, the theoretical risk of cancer acceleration, and the potential for abuse, its use must be strictly limited to controlled research settings.
DOSAGE
Dosing for MOTS-c is based on successful animal models, with human translational equivalents still being finalized in early research. The time of day for injection does not necessarily matter, but a morning injection is often preferred to take advantage of MOTS-c’s potentially energizing effects.
Administration and Frequency
-
Administration: Injections are subcutaneous (SubQ) into a fatty area such as a thigh, an upper arm, or the belly. Intraperitoneal (IP) injection is also used in research models.
-
Rotation: Providers recommend rotating your injection sites to minimize the risk of injection site reactions.
-
Frequency (Research): MOTS-c is a twice-weekly treatment, which seems more easily manageable than the near-daily injections required with other peptides (for example: CJC-1295). Research protocols often use daily or thrice-weekly administration for sustained metabolic effect.
Empirical Dosing Guidelines -
Starting Dose: A dose of MOTS-c ought to start around 5 mg per injection.
-
Dosing Range (Animal Models): High doses of 5 mg/kg to 15 mg/kg have been used in mice 3 times per week for metabolic and performance benefits.
Timeline for Benefits
-
Weeks 1–2: You may begin to feel the benefits of your treatment in as little as 1–2 weeks, as your improved metabolism and mitochondrial function lead to higher energy levels.
-
Weeks 4–6: You might notice improvements in physical performance, such as increased stamina and endurance. Meanwhile, reduced inflammation may allow you to experience a general boost in your physical and mental well-being.
RECONSTITUTION
MOTS-c is supplied as a lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder.
Reconstitution Fluid and Dilution
-
Reconstitution Fluid: Use sterile or bacteriostatic water (BAC Water).
-
Standard Dilution (EX: 10 mg Vial): For a 10 mg vial, adding 1 mL of BAC water results in a highly concentrated stock solution of 10 mg/mL.
-
Common Dilution (EX: 40 mg Vial): A common reconstitution for a 40 mg vial is to add 5 mL of bacteriostatic water. This yields a concentration of 8 mg/mL (or 8,000 mcg/mL).
Mixing Technique
-
Inject Diluent: Inject the BAC Water slowly down the side of the vial.
-
Mixing: DO NOT SHAKE vigorously. Gently swirl the vial until the powder is completely dissolved into a clear solution.
Post-Reconstitution Storage
-
Storage: Once reconstituted, the solution must be stored in the refrigerator (2°C to 8°C).
-
Stability: The solution is generally stable for 14 to 28 days under proper refrigeration.
WHERE TO BUY MOTS-C
Researchers should always vet their sources to ensure that a few key factors are present in their test subjects. With the rise in peptide popularity in recent years, many companies have created peptides that undergo little to no testing, quality standards, or regulations. As it is not regulated by the FDA, researchers must do their due diligence and look closely at the company's practices and standards.
When selecting a supplier for MOTS-c, focus on transparency and quality assurance, not customer testimonials:
- Quality Documentation: A reputable supplier must provide:
- Certificate of Analysis (COA): This document must be recent (corresponding to the batch/lot number purchased) and demonstrate a minimum purity of >95% via High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) testing.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS) Data: The COA must include mass spectrometry (MS) confirmation to verify the compound’s exact molecular weight, confirming its chemical identity.
- Contaminant Testing: Look for reports on heavy metals, microbial load, and solvent residues (e.g., residual trifluoroacetic acid, or TFA). The presence of these contaminants can severely compromise research and introduce unknown toxicity.
- Vendor Verification and Transparency
-
Specialization: Prioritize vendors who specialize in the manufacturing and distribution of peptides for academic and biotechnology research, rather than general supplement vendors.
-
Manufacturing Origin: Inquire about the source of the raw materials and the manufacturing protocols. Ideal suppliers adhere to strict quality control processes.
-
Handling & Storage: The supplier must provide clear documentation on the proper storage and handling procedures for the peptide to maintain its stability and integrity.
-
Conclusion on Procurement: Given the high risk of contamination, mislabeling, and legal ambiguity. The use of MOTS-c outside of this defined research context poses unacceptable, unquantified risks to human health.
REFERENCES
- “Mots-C.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine, pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Mots-c. Accessed 24 Nov. 2025.
- “What Is the Mots-C Peptide?: USADA.” NPC Hello, 16 Jan. 2024, www.usada.org/spirit-of-sport/what-is-mots-c-peptide/#:~:text=No%2C%20MOTS%2Dc%20is%20still,it%20is%20safe%20or%20legal.
- Min, Dan. “MOTS-C Peptide: Benefits, Safety, & Buying Advice [2025].” Innerbody, Innerbody Research, 13 June 2025, www.innerbody.com/mots-c-peptide.
- “Peptide Dosage Calculator – Easily Calculate Your Peptide Doses.” Cellgenic, 15 Jan. 2025, cellgenic.com/peptide-calculator/#:~:text=The%20amount%20of%20water%20to,of%20compounds%20with%20distinct%20effects.
-
MDPI (ID 1422-0067/23/19/11991). "$\text{MOTS-c}$, $\text{the}$ $\text{Most}$ $\text{Recent}$ $\text{Mitochondrial}$ $\text{Derived}$ $\text{Peptide}$ in $\text{Human}$ $\text{Aging}$ $\text{and}$ $\text{Age-Related}$ $\text{Diseases}$."
-
Cell Metabolism. "The $\text{mitochondrial-derived}$ $\text{peptide}$ $\text{MOTS-c}$ $\text{promotes}$ $\text{metabolic}$ $\text{homeostasis}$ and $\text{reduces}$ $\text{obesity}$ $\text{and}$ $\text{insulin}$ $\text{resistance}$."
-
ResearchGate (ID 361888985). "$\text{MOTS-c}$ $\text{increases}$ $\text{in}$ $\text{skeletal}$ $\text{muscle}$ $\text{following}$ $\text{long-term}$ $\text{physical}$ $\text{activity}$ and $\text{improves}$ $\text{acute}$ $\text{exercise}$ $\text{performance}$ $\text{after}$ $\text{a}$ $\text{single}$ $\text{dose}$."
-
Frontiers in Endocrinology (ID 10.3389/fendo.2025.1654506). "Case $\text{Report}$: $\text{Efficacy}$ and $\text{safety}$ of $\text{dose-escalated}$ $\text{Mazdutide}$..."
-
Innerbody. "$\text{MOTS-c}$ $\text{Peptide}$: $\text{Benefits}, \text{Safety}, \text{and}$ $\text{Buying}$ $\text{Advice}$."
-
USADA. "What is the $\text{MOTS-c}$ $\text{peptide}$?"
-
MDPI (ID 1422-0067/20/10/2456). "$\text{Mitochondrial-Derived}$ $\text{Peptide}$ $\text{MOTS-c}$ $\text{Increases}$ $\text{Adipose}$ $\text{Thermogenic}$ $\text{Activation}$ $\text{to}$ $\text{Promote}$ $\text{Cold}$ $\text{Adaptation}$."
The PrepTide: Disclaimer

